Sustainable Decarbonisation strategy’s for Industrial Policy
Introduction
The industrial sector is a key driver of economic growth and development in low-income countries. It creates jobs, generates income, and contributes to exports. However, many low-income countries face challenges in developing their industrial sectors, including limited access to finance, technology, and infrastructure.
One way to address these challenges is through industrial policy. Industrial policy refers to the government's use of policies and interventions to promote the development of specific industries or sectors. This can be done through a variety of means, such as providing financial incentives, investing in infrastructure, and creating regulations that support industrial development.
Demand Driven Approach
One key element of industrial policy for low-income countries is a demand-driven approach. This means that the government should focus on promoting industries that have the potential to generate demand both domestically and internationally. This can be done by identifying and supporting industries that have a comparative advantage, such as those that have access to natural resources, a skilled labor force, or a large domestic market.
Production Dividend Method
Another important aspect of industrial policy is the production dividend method. This method involves dividing the overall demand for each product among different types of industries equally. This can help to ensure that all industries have the opportunity to participate in the growth of the industrial sector.
Energy Monitoring System
Energy efficiency is a critical consideration for industrial policy in low-income countries. The government should provide fixed energy consumption for small, medium, and large industries based on the demand rate of each product. This can be done through a variety of means, such as providing free energy monitoring devices, allocating fixed electricity or energy to all industries, or providing tax incentives for energy-efficient practices.
Circular Employment
Creating employment opportunities is a key objective of industrial policy in low-income countries. The government should create employment opportunities based on the demand rate of the country. This can be done by allocating, scheduling, monitoring, and reallocating human resources or labor for each industry according to each product demand rate.
Benefits
Industrial policy can provide a number of benefits for low-income countries, including:
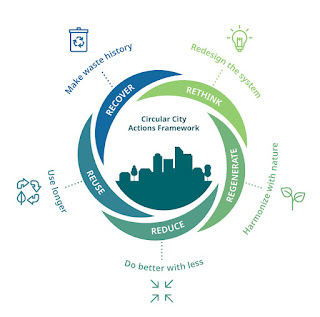
Circular Economy:
Industrial policy can help to create a circular economy by resharing the economy and industries by connecting them with a demand-driven approach.
Inclusiveness:
Industrial policy can help to increase the demand rate of each and every manufacturer and product by inclusiveness approach of every small, medium, large manufacturing industries.
These industries have the potential to generate demand both domestically and internationally, and they can also contribute to job creation and economic growth.
Policy Strategies
Demand-Driven Approach
Method 1:
Create a fixed production rate for every industry for every month according to the demand rate.
Method 2:
Increase the tax rate of every product after the demand rate for each industry is met.
Method 3:
Implement zero tax for each manufactured product under the demand-driven production rate.
Energy Monitoring System
Method 1:
Provide free live energy monitoring devices attached to every small, medium, and large industry.
Method 2:
Allocate fixed electricity or energy to all industries depending on the demand rate of the country.
Method 3:
Offer free electricity and tax exemption to all industries for all manufacturers for all products under the demand rate.
Method 4: Increase electricity prices and taxes for each industry for each product after producing a higher demand rate.
Circular Employment
*Method 1:
Demand rate = production rate = working hours. Every employee should be allocated for every manufacturing industry and product depending on the demand rate.
Method 2:
Every employee should be paid by the government if the manufacturing industry produces a product under the demand rate.
Method 3:
Every manufacturing industry should pay extra tax and salary to every employee after producing every product after the demand rate.
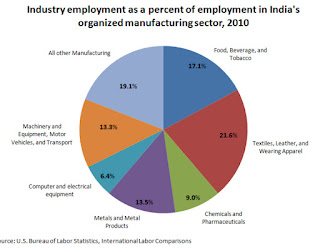
List of Industries
The following is a list of industries that are potential candidates for industrial policy in low-income countries:
Agriculture and food processing
Textiles and garments
Leather and footwear
Furniture and wood products
Metals and engineering
Chemicals and plastics
Electronics and appliances
Tourism
These industries have the potential to generate demand both domestically and internationally, and they can also contribute to job creation and economic growth.
💡Industrial Policy Framework :
Manufacturing industries in low-income countries, including India, face unique challenges. To boost their growth and competitiveness, a well-defined industrial policy strategy is crucial. Here's a breakdown:
📊 Demand-Based Allocation:
- Calculate the overall demand for manufactured goods in the country.
- Divide this demand among small, medium, and large manufacturing companies based on their production capacities and energy usage.
⚙️ Production Rate Limits:
- Set clear limits on the production rates for each category of manufacturing companies.
- This ensures balanced growth and prevents overproduction.
💡 Energy Efficiency Measures:
- Implement strict energy efficiency standards for all manufacturing companies.
- This reduces production costs and promotes sustainable practices.
Equal Carbon Emission Quotas:
- Set equal carbon emission quotas for each manufacturing category.
- This ensures balanced growth and prevents overproduction of emissions.
Neutralization Devices:
- Install carbon-neutralizing devices in all manufacturing companies.
- These devices capture and neutralize small carbon emissions from fixed production rates.
⏰ Working Hours Optimization:
- Establish optimal working hours for each manufacturing category.
- This ensures worker well-being and productivity.
🤝 Collaboration and Partnerships:
- Encourage collaboration between manufacturing companies, research institutions, and the government.
- This fosters innovation and technology transfer.
💰 Access to Financing:
- Provide financial incentives and support to manufacturing companies, especially small and medium enterprises.
- This helps them scale up production and compete effectively.
🚀 Export Promotion:
- Develop strategies to promote exports of manufactured goods from low-income countries.
- This diversifies the economy and increases foreign exchange earnings.
By implementing these measures, low-income countries like India can strengthen their industrial sectors, create jobs, and drive economic growth. #IndustrialPolicy #ManufacturingGrowth #EconomicDevelopment
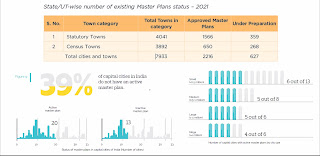
Proof of evidence : Industrial Policy for Low Income Countries and India





















%20(1).png)
Comments
Post a Comment